Obstructive Sleep Apnoea

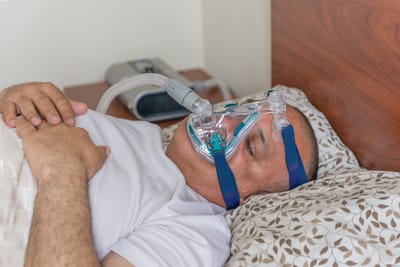
If you or someone you know suffers from OSA, it's important to understand the condition and seek treatment. Here's what you need to know:
Symptoms of OSA
The most common symptoms of OSA include loud snoring, gasping or choking during sleep, daytime sleepiness, morning headaches, and difficulty concentrating. If left untreated, OSA can lead to more serious health issues, such as depression, diabetes, and obesity.
Causes of OSA
Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by a blockage or narrowing of the airway. This can be due to a number of factors, including excess weight, a large neck circumference, or structural abnormalities in the mouth or throat. OSA is also more common in men than women, and the risk increases with age.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect that you may have OSA, it's important to speak with Dr Aldik about it. He may recommend a sleep study to determine if you have the condition. Treatment for OSA typically involves lifestyle changes, such as losing weight or quitting smoking, as well as the use of a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine to help keep the airway open while sleeping. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to correct structural issues in the mouth or throat.
Prevention
While some risk factors for OSA are out of your control, such as age and gender, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bed, and sleeping on your side instead of your back can all help to reduce your risk of OSA.
In conclusion, obstructive sleep apnea is a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for OSA, you can take steps to protect your health and ensure a better night's sleep.
Case Study: A Good Night’s Sleep Restored
Mr. A is a 40-year-old man who thought he was just “getting older.” He often felt tired during the day, struggled to stay alert, and sometimes even nodded off while watching TV.
At night, his partner noticed something — he snored loudly, sometimes stopped breathing, and would suddenly wake up gasping for air. The snoring became so disruptive that his partner eventually had to sleep in a different room.
Mr. A didn’t realise how serious this could be and put his daytime sleepiness down to age and a busy lifestyle. But when things didn’t improve, he was referred to our sleep clinic.
The sleep studyWe arranged an overnight sleep study, which showed that Mr. A had a condition called sleep apnoea. This meant his airway was collapsing while he slept, stopping him from breathing properly and preventing him from getting restful sleep.
TreatmentMr. A was started on CPAP therapy (a small machine that gently blows air through a mask to keep the airway open at night).
The resultsThe difference was life-changing. His snoring completely resolved, his partner could finally sleep in the same room again, and Mr. A woke up feeling refreshed and energetic. His daytime tiredness disappeared, and he realised how much better life could be with proper sleep.
What we can learn from his story:Snoring is not always “just snoring.” If you or your loved one notices pauses in breathing, gasping, or daytime sleepiness, it may be sleep
At night, his partner noticed something — he snored loudly, sometimes stopped breathing, and would suddenly wake up gasping for air. The snoring became so disruptive that his partner eventually had to sleep in a different room.
Mr. A didn’t realise how serious this could be and put his daytime sleepiness down to age and a busy lifestyle. But when things didn’t improve, he was referred to our sleep clinic.
The sleep studyWe arranged an overnight sleep study, which showed that Mr. A had a condition called sleep apnoea. This meant his airway was collapsing while he slept, stopping him from breathing properly and preventing him from getting restful sleep.
TreatmentMr. A was started on CPAP therapy (a small machine that gently blows air through a mask to keep the airway open at night).
The resultsThe difference was life-changing. His snoring completely resolved, his partner could finally sleep in the same room again, and Mr. A woke up feeling refreshed and energetic. His daytime tiredness disappeared, and he realised how much better life could be with proper sleep.
What we can learn from his story:Snoring is not always “just snoring.” If you or your loved one notices pauses in breathing, gasping, or daytime sleepiness, it may be sleep